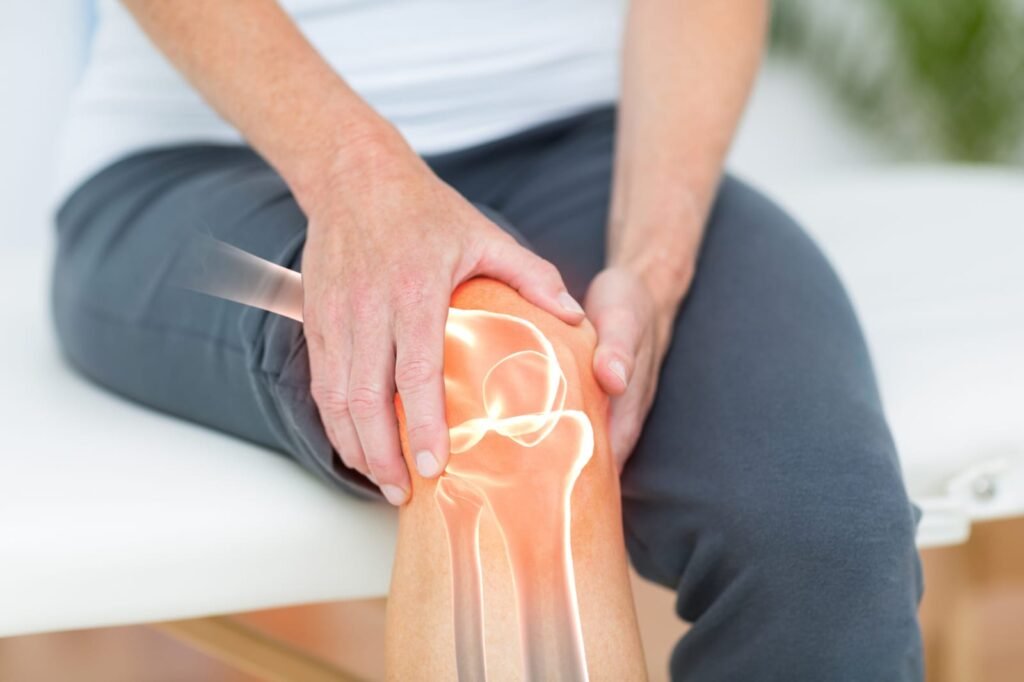
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. It is mostly associated with aging factor. It is usually low grade inflammation of the weight wearing joints results in pain and swelling. When this condition persists for a long duration can result in loss of movement, issues with gate, general feeling of not being well and disturbs a person physically and psychologically.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease. It occurs when the cartilage between bones in the joints get damaged due to degenerative changes. Cartilage cushions the bones from rubbing against each other’s surface while various movements. In case OA this cushion gets deteriorate and cause frictions on the movements and results is inflammation called arthritis. Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis. It is mostly associated with aging factor. It is usually low grade inflammation of the weight wearing joints results in pain and swelling. When this condition persists for a long duration can result in loss of movement, issues with gate, general feeling of not being well and disturbs a person physically and psychologically.
When we see in Ayurveda about joint diseases, Osteoarthritis can be co- related to Sandhivata or sandhigat vata.
Let’s understand what Sandhivata is: It is a disease caused by the vitiated vata dosha (Vatavyadhi). It being a Vatavyadhi, located in vital points, bones and joints (Marmasthisandhi), and its occurrence in old age makes it difficult to cure (Kashtasadhya). Vata Dosha plays main role in this disease, cause lots of pain and discomfort (Shula Pradhana Vedana ) is the cardinal feature of the disease associated with swelling (Sandhishotha) and a feeling of joint got filled with air (Vata Purna Druti Sparsha), lack of movements or painful movement of the joints.
Let’s understand what happens actually during the encounter with Sandhivata: Due to the vata vitiation (vata vitiating food and life style) and with the aging (natural increase in vata dosha due to dhatu kshaya),vata moves from its place and get lodged in the joints and give rise to disease, called Sandhivata or sandhigat vata. For the better understanding, it can be explain this way that, due to vata aggravation factors like age, degenerative changes, old injuries, unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy or improper food /nourishment, there is drying up of synovial fluid, and loss of cartilage tissue. This cartilage tissue on the bone surface and synovial fluid prevents friction while movements of joints and in the absence of these bones get rubbed and get damaged leads to sever inflammation of joints.
Factors that increase the risk of osteoarthritis include:
- Old age – With the age degenerative changes takes place and risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
- Gender – Women are more prone to develop osteoarthritis, as hormonal changes takes place during and post menopausal phase.
- Congenital deformities – Few people are born with malformed joints or defective cartilage can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Injuries – Injuries, to bones or joints may increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Obesity – Carrying more body weight put more stress on weight-bearing joints and can aggravate joint issues.
- Lack of exercise – exercise is necessary for the proper circulation around the joints.
- Occupations – Osteoarthritis can be occupational hazard.
- Secondary to diseases – Diabetes, underactive thyroid, gout or Paget’s disease of bone can increase your risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Family history – Family history add to certain extend to this disease.
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis:
Mostly clinical symptoms and signs are sufficient to diagnose OA or a physical examination by a physician can detect it easily. Other advance measure are there may be needed in case of complexity. X-rays, arthroscopy, ultrasound, MRI, CT scan etc. are used specially for X-rays is the main diagnostic tool among all, it shows the extent of joint deterioration, including narrowing of joint space, thinning or erosion of bone, excess fluid in the joint, and bone spurs or other abnormalities.Now let us know the line of treatment or management of this degenerative arthritis:
Approach towards treating or healing osteoarthritis should be comprehensive and complete. Hence here at Ketav’s Ayush health Paradise we do Shodhna chikitsa (Purification treatment), Shamna chikitsa (Palliative treatment) both by external and internal routes. Along with this we follow a planed protocol of oral medicines, diet & life style and Rasayana therapies to give the maximum possible benefits to the patients. In case of degenerative disease early diagnosis and treatment is the key to control the progression and heal the damages. So depending upon the severity and damages to the joints we plans 15 to 21 days Panchkarma therapies. During these days we plan therapies to achieve maximum healing and the following objectives;
- Set up the dosha equilibrium in the body.
- Improve the circulation around the joints.
- Reduce the inflammation within and surrounding the joints.
- Improve the range of movement by nourishing therapies.
- Stabilize the affective joints by anti inflammatory treatment.
- Repair the wear tare to the rejuvenating therapies.
We would say as one gets encountered with this degenerative disease, the first and foremost thing is to stop further progression or the damage to the joints. Otherwise OA make you cripple and dependent, if you don’t take care at right time. With the passage of time degenerative changes increase and your mental health also get affected with the physical ailment. Early detection followed by right kind of treatment, one can stop or slow down the disease pathology. This OA associated with the age factor and degenerative in nature, it is stubborn kind of disease hardly get controlled with oral medications. Classical Ayurvedic therapies can do wonder to pacify the symptoms and stop the degenerative changes. Ayurvedic panchkarma therapies work on alleviation of root cause of the disease.
Few Dos and Don’ts as per Ayurveda may help in OA
Do’s:
- Intake of Madhura (sweet), Amla (sour), Lavana (salt) and Snigdha (unctuous) food, Garlic, Ginger, Asafetida, Black pepper spices etc
- Regular habit of exercising
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Practice all kind of movements of the joints
- Wholesome diet
- Protect any injury to the joints to prevent further damage
Don’ts:
- Long fasting and excess of heavy food
- Awakening at night (Ratri jagaran)
- Suppression of natural urges( Vega-vidharana)
- Stress physical and mental
- Prolonged standing
- Over exertion and injury to joints
Recommended Ayurvedic medicines
“We Aware, early diagnosis and a right treatment planning can save your joints”
By
Dr Seema Santoshi
Panchkarma specialist
BAMS, CGO, YFC
PGDPSM.